Yungi Kwon, Sungwook E. Hong, Inkyu Park
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 77(July 2020), 49-59
Abstract
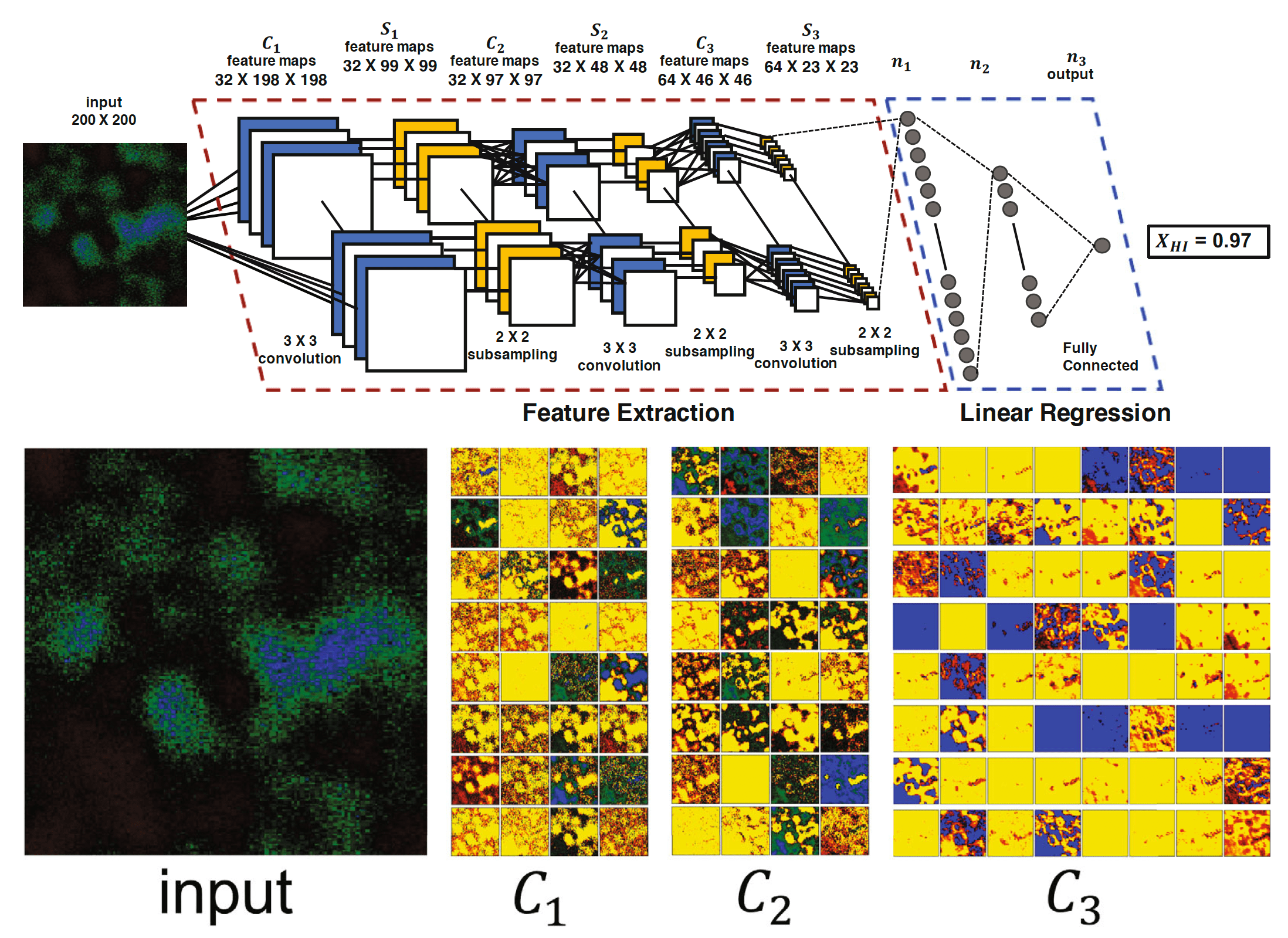
We propose a deep learning analysis technique with a convolutional neural network (CNN) to predict the evolutionary track of the Epoch of Reionization (EoR) from the 21-cm differential brightness temperature tomography images. We use 21cmFAST, a fast semi-numerical cosmological 21-cm signal simulator, to produce mock 21-cm maps between z = 6–13. We then apply two observational effects, such as instrumental noise and limit of (spatial and depth) resolution somewhat suitable for realistic choices of the Square Kilometre Array (SKA), into the 21-cm maps. We design our deep learning model with CNN to predict the sliced-averaged neutral hydrogen fraction from the given 21-cm map. The estimated neutral fraction from our CNN model has great agreement with the true value even after coarsely smoothing with broad beam size and frequency bandwidth and heavily covered by noise with narrow beam size and frequency bandwidth. Our results show that the deep learning analyzing method has the potential to reconstruct the EoR history efficiently from the 21-cm tomography surveys in future.