Stephen Appleby, Changbom Park, Sungwook E. Hong, Ho Seong Hwang, Juhan Kim
The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 896(2)(June 2020), 145
Abstract
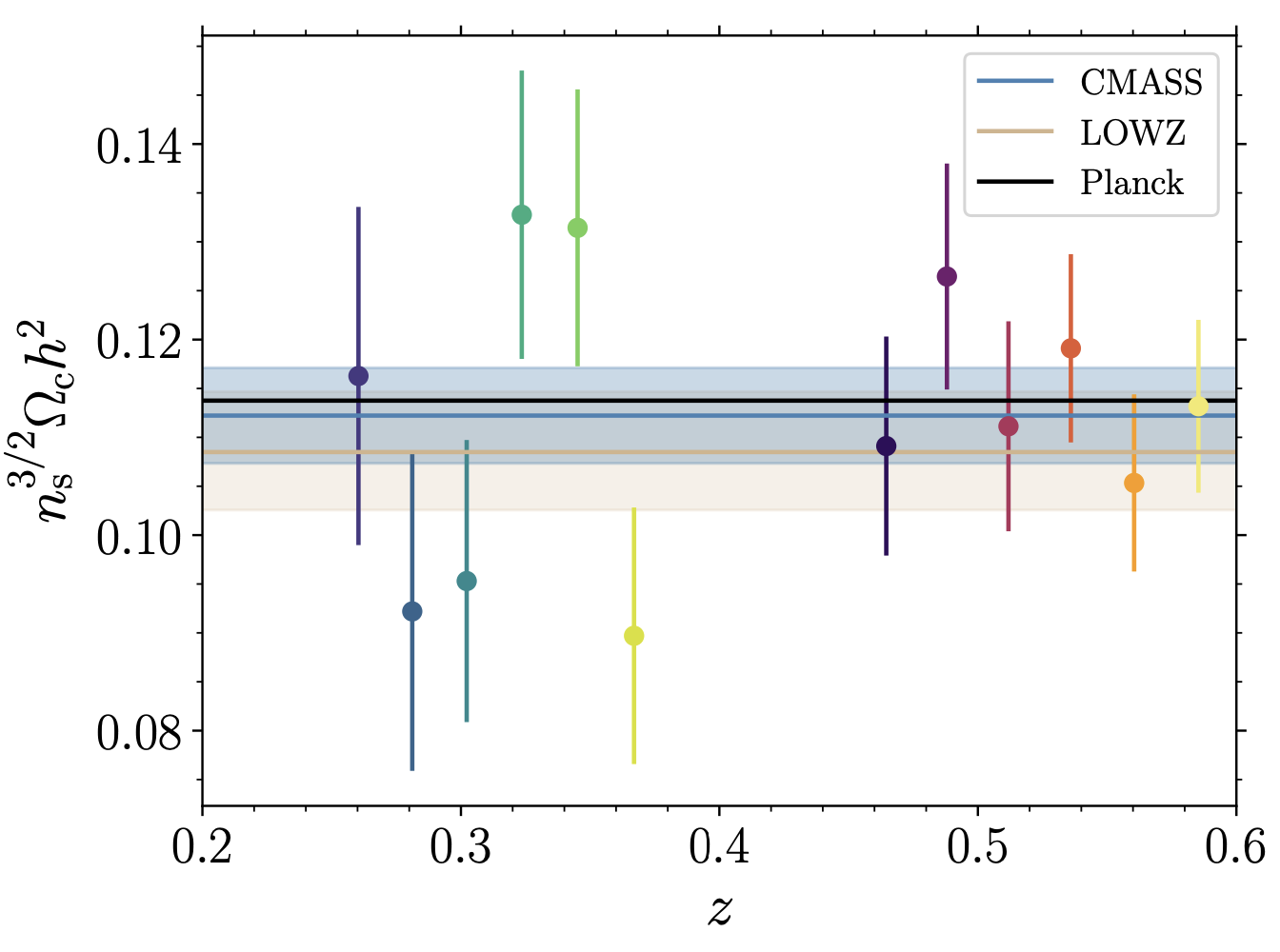
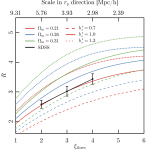
We present measurements of the two-dimensional genus of the SDSS-III BOSS catalogs to constrain cosmological parameters governing the shape of the matter power spectrum. The BOSS data are divided into twelve concentric shells over the redshift range 0.2<z<0.6, and we extract the genus from the projected two-dimensional galaxy density fields. We compare the genus amplitudes to their Gaussian expectation values, exploiting the fact that this quantity is relatively insensitive to non-linear gravitational collapse. The genus amplitude provides a measure of the shape of the linear matter power spectrum, and is principally sensitive to Ωch2 and scalar spectral index ns. A strong negative degeneracy between Ωch2 and ns is observed, as both can increase small scale power by shifting the peak and tilting the power spectrum respectively. We place a constraint on the particular combination n3/2sΩch2 — we find n3/2sΩch2=0.1121±0.0043 after combining the LOWZ and CMASS data sets, assuming a flat ΛCDM cosmology. This result is practically insensitive to reasonable variations of the power spectrum amplitude and linear galaxy bias. Our results are consistent with the Planck best fit n3/2sΩch2=0.1139±0.0009.